South Korea ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) Therapeutic Market Analysis
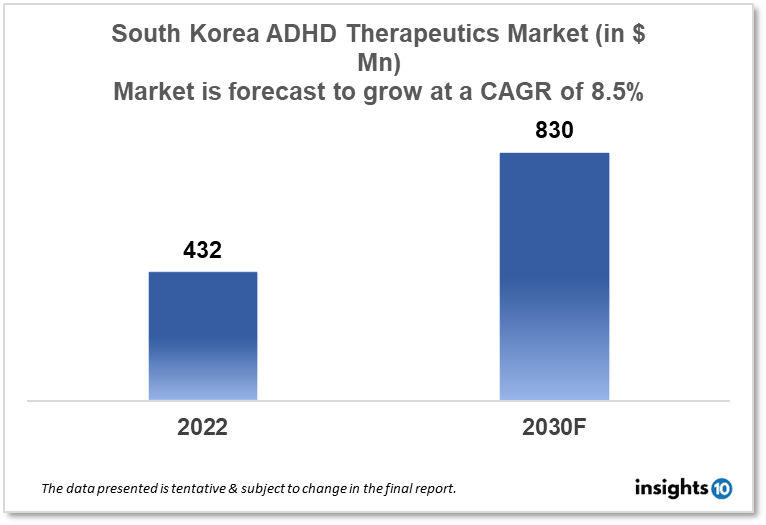
South Korea Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) therapeutics market is projected to grow from $432 Mn in 2022 to $830 Mn in 2030 with a CAGR of 8.5% for the year 2022-30. The increasing awareness about ADHD in South Korea and rising R&D efforts taken by the pharma companies are the driving factors for the growth of the market. The South Korea ADHD therapeutics market is segmented by drug, drug type, demographics, and by distribution channel. Some of the key players in the market include Hanmi Pharma, Daewoong Pharma, and Eli Lilly.
Buy Now

South Korea Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Therapeutics Market Executive Analysis
The South Korea Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) therapeutics market size is at around $432 Mn in 2022 and is projected to reach $830 Mn in 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 8.5% during the forecast period. A record-breaking national budget of $496 Bn has been developed for South Korea for 2022. It established the first additional funding for this year in February, totaling $13 Bn, to assist businesses affected by the pandemic. A large portion of the total, or 35.4%, was given to programs for public health, welfare, and jobs. As the population has aged and the welfare system has been extended, South Korea's government debt-to-GDP ratio has steadily increased, reaching an estimated 49.7% this year from below 40% in 2019 and below 30% in 2010.
In children between the ages of 5 and 15 years, ADHD is one of the most prevalent mental disorders; it impacts 8%-12% of children globally. In terms of monetary costs, stress on families, disruption of academic and professional pursuits, as well as detrimental effects on self-esteem, it has a significant influence on society. Studies conducted in South Korea have linked ADHD to genetic predispositions, exposure to chemicals in the environment, and co-morbidity with other psychiatric illnesses. Despite only being studied in Seoul, the prevalence of ADHD in children was found to range between 5.9% and 9.0%. According to previous studies, the prevalence of adult ADHD in South Korea was estimated to be 2.5%. Childhood ADHD symptoms have been found to persist into adulthood at a rate of about 50%. Nevertheless, symptom domain-specific declining patterns in symptom severity vary. Contrary to how early in childhood hyperactivity and impulsivity improve, the period and rate of improvement in inattention symptoms show later and improve at a slower rate.
Patients who were diagnosed with ADHD as children or adolescents can continue receiving regular therapy as adults, per the current clinical practice in South Korea. Many adult ADHD patients are treated by general practitioners after having ceased receiving treatment following their initial diagnosis in childhood or adolescence and starting it again years later. They also take care of patients who need treatment as adults but did not receive the proper help when it was needed. The risk of adverse outcomes in mental and physical health due to ADHD may be decreased with early and sufficient intervention. Non-pharmacological, pharmacological, or a mix of the two are all possible treatment modalities. The first entails psychosocial, cognitive, and behavioral training that energizes neuropsychological domains linked to ADHD, such as executive and cognitive processes.
In general, stimulants outperform other medications in terms of effectiveness across all age groups. Amphetamines among the stimulants have demonstrated larger impact sizes in reducing the symptoms of ADHD than methylphenidate. Although their mechanisms of action are somewhat different, methylphenidate and amphetamines both have effects that increase the availability of dopamine and norepinephrine in the synaptic cleft, resulting in improved neurotransmission. Methylphenidate's pharmacological action is primarily caused by its blocking of the dopamine and norepinephrine transporters (DAT and NET, respectively), which prevents these neurotransmitters from being taken up again by presynaptic neurons.
Market Dynamics
Market Growth Drivers
In South Korea, there is a rising consciousness of ADHD, which has increased the number of diagnoses. There is a corresponding rise in demand for ADHD medications as more people become conscious of the condition. ADHD is now more easily recognized in both children and adults as a result of improved diagnostic methods and instruments. As a consequence, diagnoses are now more precise, and the demand for ADHD medications has increased. Major pharmaceutical firms are making significant investments in research and development as a result of realizing the market potential for ADHD in South Korea. New treatments and medicines have been made available as a result, spurring the South Korea ADHD therapeutics market expansion.
Market Restraints
Despite increased awareness of the condition, South Korea still has some societal stigma associated with it. This could discourage some individuals from getting treatment and restrict the South Korea ADHD therapeutics market expansion. The South Korean government is aggressively attempting to reduce healthcare expenses, which could put pressure on the cost of ADHD medications. This may reduce pharmaceutical firms' profitability and slow market expansion. Pharmaceutical companies are expected to become more competitive as the ADHD market in South Korea expands. This might result in reduced prices and profit margins, which might slow market expansion.
Competitive Landscape
Key Players
- Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceutical (KOR)
- Samsung Biologics (KOR)
- SK Chemicals (KOR)
- Hanmi Pharm (KOR)
- Daewoong Pharma (KOR)
- Eli Lilly
- Perdue Pharma
- Johnson and Johnson
- Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Takeda
- GlaxoSmithKline
Healthcare Policies and Regulatory Landscape
The safety and effectiveness of medicines and medical equipment in Korea are regulated by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS), formerly the Korea Food & Drug Administration (KFDA). There are five divisions in the MFDS. The two departments in charge of overseeing pharmaceutical and medical device regulations are the Pharmaceutical Safety Bureau and the Medical Device Safety Bureau. For the purpose of ensuring the safety of food and drugs, the MFDS is in charge of developing and implementing policies and laws. Its responsibilities include carrying out safety assessments, establishing safety requirements, carrying out inspections and investigations, giving licenses and permits, and enforcing rules. In order to react to public health emergencies and outbreaks, the MFDS coordinates closely with other governmental organizations, such as the Korea Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (KCDC). In order to promote global food safety and share information on best practices, it also works with international organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
1. Executive Summary
1.1 Disease Overview
1.2 Global Scenario
1.3 Country Overview
1.4 Healthcare Scenario in Country
1.5 Patient Journey
1.6 Health Insurance Coverage in Country
1.7 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API)
1.8 Recent Developments in the Country
2. Market Size and Forecasting
2.1 Epidemiology of Disease
2.2 Market Size (With Excel & Methodology)
2.3 Market Segmentation (Check all Segments in Segmentation Section)
3. Market Dynamics
3.1 Market Drivers
3.2 Market Restraints
4. Competitive Landscape
4.1 Major Market Share
4.2 Key Company Profile (Check all Companies in the Summary Section)
4.2.1 Company
4.2.1.1 Overview
4.2.1.2 Product Applications and Services
4.2.1.3 Recent Developments
4.2.1.4 Partnerships Ecosystem
4.2.1.5 Financials (Based on Availability)
5. Reimbursement Scenario
5.1 Reimbursement Regulation
5.2 Reimbursement Process for Diagnosis
5.3 Reimbursement Process for Treatment
6. Methodology and Scope
ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) Therapeutic Market Segmentation
By Drug Type (Revenue, USD Billion):
- Stimulants
- Amphetamine
- Methylphenidate
- Dextroamphetamine
- Dexmethylphenidate
- Lisdexamfetamine
- Others
- Non-Stimulants
- Atomoxetine
- Bupropion
- Guanfacine
- Clonidine
By Age Group (Revenue, USD Billion):
- Pediatric And Adolescent
- Adult
By Distribution Channel (Revenue, USD Billion):
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Speciality Clinics
- Retail Pharmacies
- e-Commerce
By Psychotherapy (Revenue, USD Billion):
- Behaviour Therapy
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
- Interpersonal Psychotherapy
- Family Therapy
Insights10 will provide you with the reports within 10 key parameters which are:
- Market Overview
- Market Growth Drivers & Restraints
- Epidemiology of Disease Type
- Market Segmentation
- Market Share
- Competitive Landscape
- Key Company Profiles
- Healthcare Policies & Regulatory Framework
- Reimbursement Scenario
- Factors Driving Future Growth
Based on our many years of experience, we believe that these are the parameters that are critical to decision-making for business stakeholders. Our focused approach to developing reports focused on 10 key parameters, enabled us to arrive at the name “Insights10”.

Stage I: Market Data Collection
Primary Interviews: We have developed a network of experts, freelancers, and researchers across countries through which we engage with local experts to gather key data points and assumptions about each market. We also engage regularly with some of the best market research agencies such as Atheneum, GuidePoint, GLG, etc. to conduct surveys and interviews, and build intelligence. We have language translators as a part of our team, who between them can cover 30+ languages allowing us to extract better local insights.
Secondary Data Collection: We have developed strong expertise and experience in secondary data collection methods for developing unique data sets and research material. We gather data from multiple reliable sources to maintain a high level of accuracy and consistency. The market data is analyzed and forecasted using appropriate statistical and coherent models. The report offers an overall analysis of the market size, growth, and market share as well as a segment-level analysis of the specific market. Our report includes precise, to-the-point information related to the overall market, competition, growth drivers, challenges, regulatory updates, and competition.
Data Sources: We have access to multiple highly reliable free and subscription data sources. We have many years of experience to understand which sources are more dependable for what and which to prefer for the reliable and latest information. The key sources of information include the following, but are not limited to:

Stage II: Market Data Analysis and Statistical Model
Market Trends: We generally look at macro parameters and micro indicators. The macro parameters include changes in government policies, demand and supply of the market, government intervention programs, and major market share. The micro indicators are GDP growth, market size, market volume, etc. We also understand nuances specific to each country like the US, Canada, India, Germany, etc., and have worked across 60+ countries and hence not only understand global trends but how these differ by country, how payment models, market structure, cultural parameters, etc. differ in each country.
Market Sizing and Analysis: Our expert data analytics team has created various market forecast models by employing the top-down approach i.e. starting with the large overall market and segmenting different areas and the bottom-up approach i.e. starting with population and epidemiology and rolling up based on spend, etc., estimating the size of the market, and distributing among the geographic and/or product segments.
The top-down approach is mainly used for new product forecasting and the bottom-up approach is used for demand estimation of any product for different countries summed up to form the total market. We are able to round off insights and build stronger forecasts because we always do both these methods and triangulate the final numbers.
The study on the market covers the analysis of the leading geographies such as Asia-Pacific, Africa, Europe, Middle East, North America, and Latin America for the period of 2022 to 2030. The qualitative analysis covers the industry landscape and trends, market opportunities, competitive landscape, and policy and regulatory scenario, and the quantitative analysis covers different market estimates and forecasts.
Data Triangulation & Validation:
Data triangulation of various sources and results of the research are carried out by benchmarking with reliable sources such as industry statistics, statistical databases, and company-level averages, etc.
We make sure to finalize the numbers in alignment with the market research. Firstly, our internal experts ensure thorough validation and checking to ensure accurate and precise analysis and then validation is also done using a multiple-data analysis model. Two-level validation is done and entails the finalization of the report scope and the way of representation pattern.
(1).png)
Stage III: Interpretation and Presentation
Analysis & Interpretation: The information gathered is then analyzed and synthesized. The second series of interviews are done if necessary to check and validate. The future opportunities are analyzed by understanding product commercialization and many other factors. It also comprises the analysis of data discrepancies observed across various data sources. Information procured from secondary and primary results is then, interpreted by considering the following parameters: (a partial list)
- Establishing market drivers and trends
- Analyzing the regulatory landscape to understand future growth
- Market Segment based analysis to obtain revenue/volume
- Analyzing current needs and determining penetration to estimate the market
Insights: Our reports deliver actionable insights backed with supporting facts and figures to assist you in achieving exemplary growth. Our in-depth analyses are interspersed with relevant insights and statistics to offer an executive-level view of a given market. The description helps in correlating many minor factors affecting the market and their impact on the different segments within the market.
Data curated from the analysis and interpretation are drawn to portray all in one consolidated report.
Presentation & Reporting: The market research report is presented in different forms such as charts by using a scientific approach for easy understanding. Historic, current, and future analysis is provided for each market in terms of both value and volume. The size of the market is interpreted in the US Dollar value and the respective unit, based on the product, for volume consumption.
The foreign exchange rates are calculated on the respective dates and for the respective regions covered in the study.
To request a free sample copy of this report, please complete the form below.
We value your inquiry and offer free customization with every report to fulfil your exact research needs.
This report addresses
- Intelligent insights to take informed business decisions
- Qualitative, acute and result oriented market analysis
- Market size and forecasts from 2022 to 2030
- Opportunities for expansion and in-depth market analysis
- Segmentation and regional revenue forecasts
- Analysis of the market share and competitive landscape
- Strategic Recommendations to chart future course of action
- Comprehensive Market Research Report in PDF and PPT formats
Need more?
- Ask our analyst how this study was put together to learn more
- Discuss additional requirements as part of the free customisation
- Add more countries or regions to the scope
- Get answers to specific business questions
- Develop the business case to launch the product
- Find out how this report may influence your business revenue


